EV용 고성능 그래핀 나노튜브 배터리
자동차 산업은 내연기관차(ICE)에서 전기차(EV)로 전환하고 있으며 EV의 핵심 요소는 리튬 이온 배터리입니다. 자동차 산업은 오랫동안 차세대 리튬 이온 배터리를 구동하는 기술을 찾고 있습니다.
그래핀 나노튜브- 주요 배터리 문제의 대한 해결책입니다
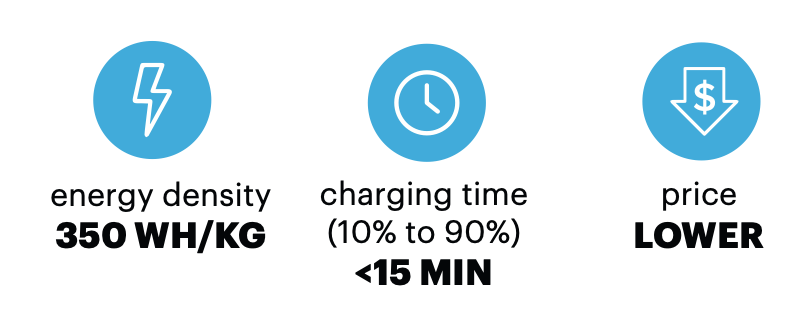
TUBALL™ 그래핀 나노튜브는 에너지 밀도, 충전 속도, 사이클 수명 및 비용 등과 같은 리튬이온전지의 주요 파라미터를 개선할 수 있는 솔루션입니다.
TUBALL™로 실리콘 음극 대량 생산 가능
배터리 충·방전 시, 실리콘 부피가 팽창하는 근본적이고 해결되지 않은 문제가 있으며, 이는 실리콘 물질 입자 간의 손실과 균열로 이어집니다.
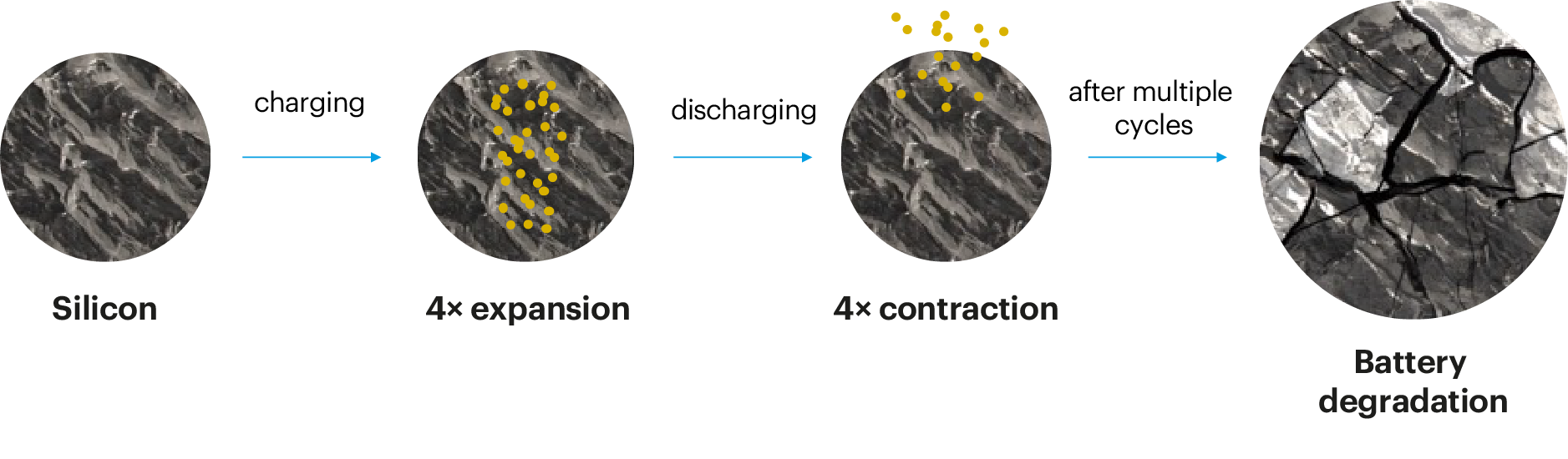
TUBALL™ 그래핀 나노튜브는 심각한 부피 팽창과 균열에도 실리콘 음극 입자가 서로 잘 연결되도록 길고 유연하며 전도성이 높고 튼튼한 내구성을 만들어 내는 유일한 소재 입니다.
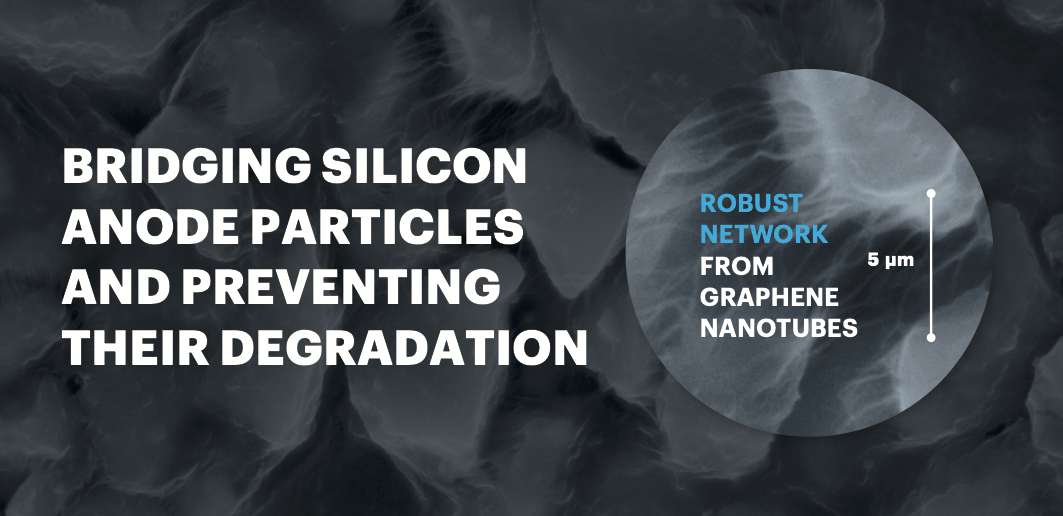
또한 TUBALL 제품을 사용하면 음극이 수명을 향상되어 엄격한 EV 제조업체 요구 사항도 충족시킬 수 있습니다.
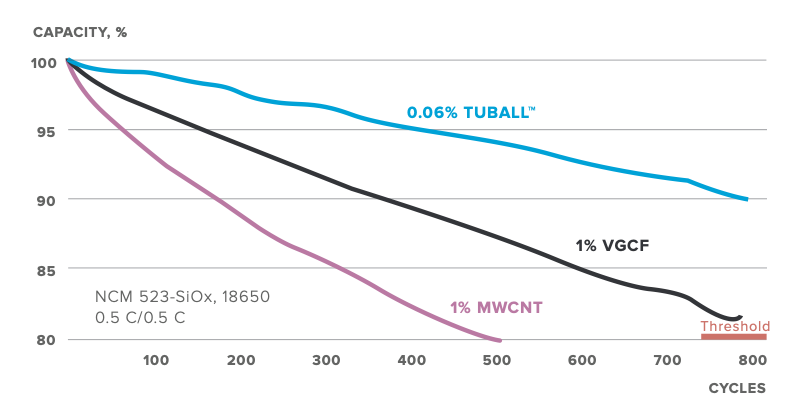
TUBALL™ 네트워크는 실리콘 기반의 음극 사이클 수명을 최대 4배 이상 증가합니다
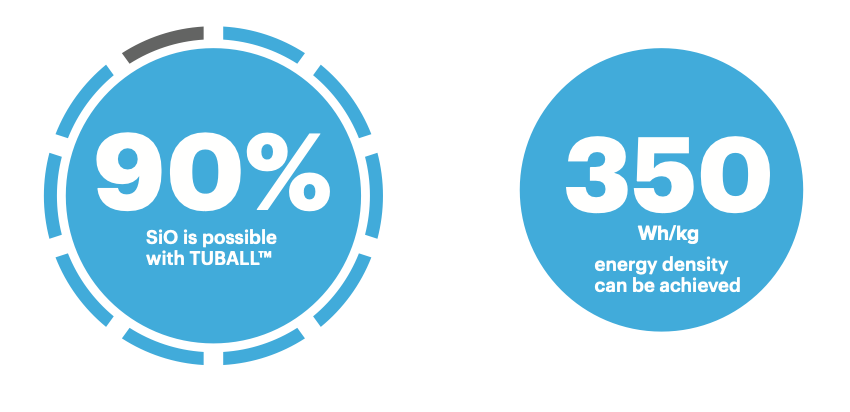
주요 리튬이온전지 생산업체들은 TUBALL™ 그래핀 나노튜브를 적용하여 20%의 Si가 내장된 음극을 만들어 최대 300 Wh/kg 및 800 Wh/l의 기록적인 배터리 에너지 밀도에 도달할 수 있다는 것을 입증했습니다. 이 배터리 셀은 현재 시장에 나와있는 최고의 리튬이온전지셀 보다 최대 +15% 더 높은 범위를 제공할 수 있습니다.
OCSiAl R&D 팀의 결과에 따르면 TUBALL 제품을 사용하면, 음극의 SiO 함량을 90%까지 증가할 수 있습니다.
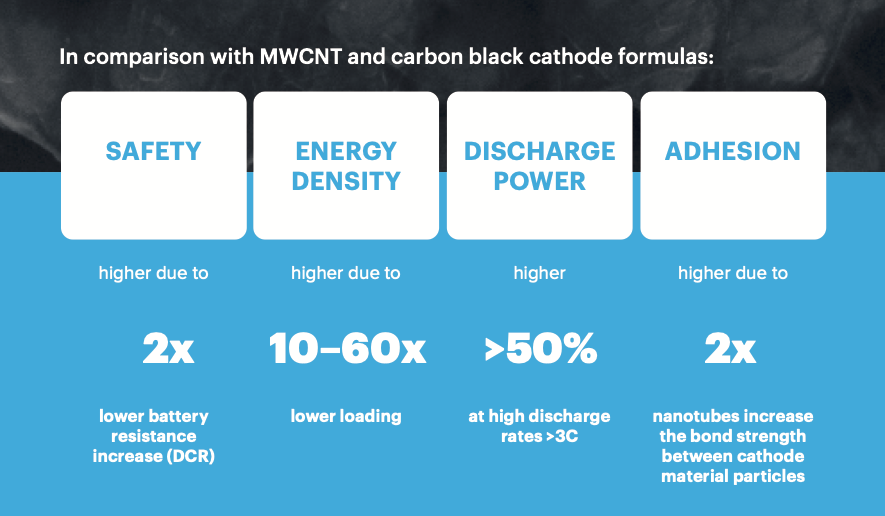
TUBALL™을 양극에 적용하면, 핵심 배터리 파라미터를 개선할 수 있습니다
그래핀 나노튜브의 고유한 특성 때문에 방전 전력, 에너지 밀도, 접착력 및 안전성 등 향상된 리튬이온전지 성능을 제공합니다. 이러한 리튬이온전지 양극 성능 개선 부분에 있어서는 탄소블랙이나 다중벽 탄소 나노튜브과 같은 기존 첨가제로는 입증할 수 없습니다.
Explore more on TUBALL™ in anodes and cathodes.
TUBALL™ 그래핀 나노튜브: 적용 방법
세계 최대 그래핀 나노튜브(=단일벽 탄소 나노튜브) 제조사인 옥시알은 음극과 양극을 위한 사용이 용이한 솔루션을 개발했습니다. TUBALL™ BATT 은 물 또는 NMP에 잘 분산된 나노튜브가 포함돼 있으며, 표준 분산 공정에서 간단히 혼합할 수 있습니다
Related videos:
How do nanotubes work inside an electrode?
Contact us to discuss your project specifications or to request a sample
Scientific validation
Silicon Single Walled Carbon Nanotube-Embedded Pitch-Based Carbon Spheres Prepared by a Spray Process with Modified Antisolvent Precipitation for Lithium Ion Batteries

The pitch-derived soft carbon and SWCNTs provided an excellent conductivity, and the porous structure of the composite accommodated the stress produced by the Si expansion.
High areal capacity battery electrodes enabled by segregated nanotube networks

High thickness and specific capacity leads to areal capacities of up to 45 and 30 mAh cm−2 for anodes and cathodes, respectively. Combining optimized composite anodes and cathodes yields full cells with state-of-the-art areal capacities (29 mAh cm−2) and specific/volumetric energies (480 Wh kg−1 and 1,600 Wh l−1).
All-Nanomat Lithium-Ion Batteries: A New Cell Architecture Platform for Ultrahigh Energy Density and Mechanical Flexibility
The all‐nanomat full cell shows exceptional improvement in battery energy density – 479 Wh/kg battery, and Si-anode capacity – 1166 mAh/g.
Optimization of Graphite–SiO blend electrodes for lithium-ion batteries: Stable cycling enabled by single-walled carbon nanotube conductive additive

The use of SWCNT conductive additive enables graphite-free SiO electrodes with 74% higher volumetric energy and superior full-cell cycling compared to graphite electrodes.
Self-transforming stainless-steel into the next generation anode material for lithium ion batteries
Areal capacities greater than 10 mAh/cm2 and volumetric capacities greater than 1400 mAh/cm3 can be achieved.
Rational design of a high-energy NCA cathode for Li-ion batteries
Replacing Denka black with SWCNT allows to reduce the carbon content to 0.2 wt% to further increase the energy density, and 2 wt% of PVDF was shown to benefit the cycling stability due to the mitigated PVDF-induced side reactions from its direct contact with NCA particles.

