Batteries
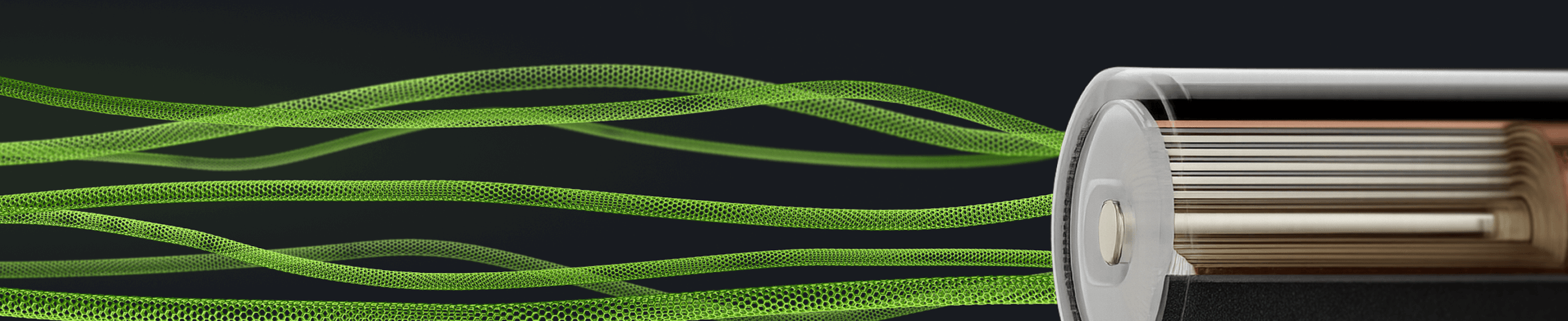

The one material
for batteries
TUBALL single wall carbon nanotubes (SWCNTs) stand out among conductive agents for batteries for their exceptional intrinsic properties, being nature’s longest and most flexible material for conductivity and reinforcement of electrodes.

TUBALL™ networks form robust electrode connections, which are essential for the performance of all key battery chemistries.
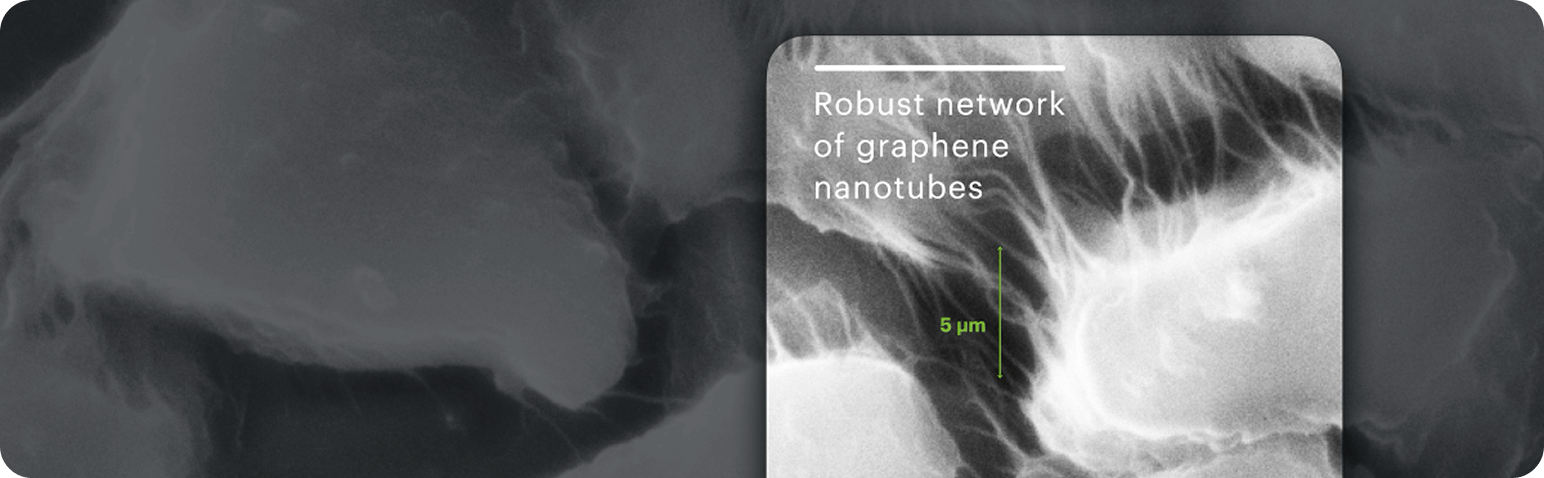
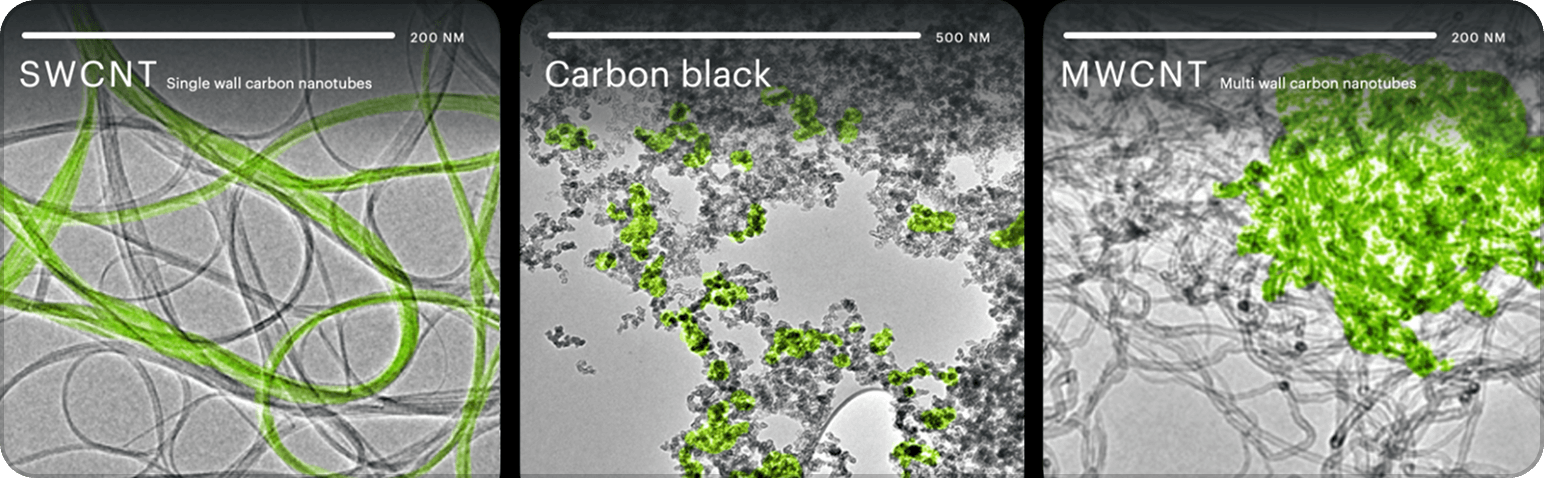
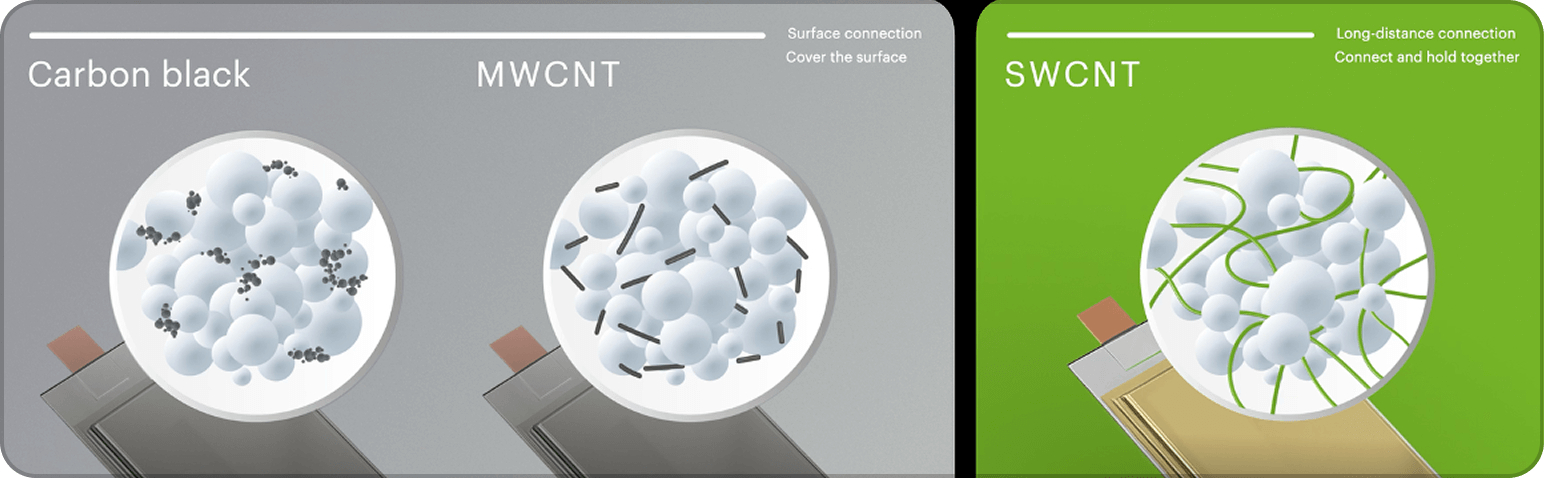
Nanotube’s unique properties result in different behavior in electrodes. While multi wall carbon nanotubes and carbon black provide only surface connections with short-distance conductivity—resulting in higher electrode bulk resistance and unstable connections—single wall carbon nanotubes create robust, long-distance connections that are stable despite active material volume expansion during long-term cycling.
Automotive

Graphene nanotubes for next-gen automotive: functionality and energy efficiency
The transport of the future requires new materials that will make vehicles intelligent, functional, and energy-efficient. Revolutionary graphene nanotube-based solutions for the automotive industry meet this challenge, driving forward the sustainable transformation. Graphene nanotubes help automotive manufacturers to optimize cost-efficiency and improve the performance of various car components. The use of elastomers, thermoplastics, and thermosets reinforced with graphene nanotubes expands the limits on the development of completely new cars with lightweight bodies; safe and energy-efficient tires; smart interiors; and long-lasting, high-performance batteries for EVs.
Extraction
and Processing
Graphene nanotubes for extraction and processing: stable ESD protection with enhanced durability
In extraction and processing sectors such as oil & gas, mining, and chemical production, equipment operates under extreme conditions, including corrosion, abrasion, chemical exposure, and high temperatures. Graphene nanotubes provide materials with reliable, electrostatic discharge protection, preventing sparks that pose serious risks in ATEX-sensitive atmospheres, while preserving high durability and strong mechanical performance.
Packaging and Storage
Graphene nanotubes for packaging and storage: functionality with comfort and aesthetics
Anti-static packaging is essential for protecting flammable materials, sensitive electronics, and personnel from electrostatic discharge during transport, handling, or storage. Graphene nanotube–enhanced anti-static materials safely dissipate static charges through stable, humidity-independent conductivity, preventing sparks that could ignite explosive atmospheres or damage electronics. At ultralow dosages, nanotubes maintain material strength, flexibility, and color, ensuring durable ESD protection without compromising performance or appearance.
Personal Protective Equipment

Graphene nanotubes for PPE: compliance with ESD standards and improved functionality
Compliance with the ESD protection requirements of international standards is crucial for personal protective equipment (PPE) to guarantee safety in hazardous environments and static-sensitive facilities, including in ATEX zones, automotive and electronics manufacturing, cleanrooms, oil & gas, and mining, chemical, pharmacy, and medical facilities. Graphene nanotubes ensure compliance with ESD safety standards, providing stable, humidity-independent electrical resistance to all elements of the uninterrupted grounding chain of ESD-safe clothing.
Sports, Leisure,
and Consumer Goods

Graphene nanotubes—the ultimate additive for sports, leisure, and consumer goods
Everyday sports and leisure products demand function, comfort, durability, and style. Graphene nanotubes add advanced performance and extended functionality by delivering stable, long-lasting electrical conductivity that remains unaffected by humidity, time, or movement—all while preserving softness, flexibility, and a wide range of colors and designs.
Medicine and Healthcare

Graphene nanotubes for medicine and healthcare: precise diagnostics with touch comfort and skin cleanliness
Healthcare devices like wearable electronics, body sensors, bionic prostheses, and massage tools rely on key features: electrical conductivity, elasticity, and softness. These devices must deliver accurate data and signals to and from the human body without causing discomfort and irritation or leaving marks on the skin.
Graphene nanotubes ensure RoHS compliance, provide precise conductivity for accurate sensor measurements, and maintain flexibility and softness — all without compromising skin comfort and device durability.
Printing

Graphene nanotubes for industrial printing: high process quality and extended equipment life
As modern printing processes become faster and more automated, they require safer, more functional, and more durable materials and components. Controlled conductivity helps dissipate static electricity, improving ink transfer, reducing dust attraction, enhancing print quality, and minimizing defects during high-speed printing.
Graphene nanotubes are an advanced anti-static additive for printing components due to their exceptional morphology and properties. When incorporated into rollers, sleeves, blankets, and pads, graphene nanotubes provide uniform and stable electrical conductivity while preserving strong mechanical performance, maintaining a clean product surface, and increasing the lifetime of these components.
Electronics and semiconductors
Graphene nanotubes for electronics and semiconductors: precise signal transmission and reliable ESD protection
Electrical conductivity is a critical factor in the electronics and semiconductor industries, directly influencing device performance, reliability, and miniaturization. As components continue to shrink and circuit density increases, even minor charge accumulation or signal loss can lead to failures, yield loss, or long-term reliability issues.
Graphene nanotubes play a key role in meeting these challenges by providing permanent electrical conductivity at ultralow loadings in various materials. Their stable 3D conductive networks enable precise signal transmission, effective ESD protection, and contamination-free performance, while preserving mechanical properties, color, and processability. As a result, graphene nanotubes support the development of smaller, faster, more reliable, and more versatile electronic and semiconductor technologies.
Construction and Infrastructure

Graphene nanotubes for construction and infrastructure: reliable ESD protection with long-lasting strength
As construction and infrastructure projects become more complex, automated, and performance-driven, advanced materials are becoming increasingly critical. Modern infrastructure requires solutions that combine long service life, enhanced functionality, and a high level of safety, including reliable electrostatic discharge protection. Graphene nanotubes address these needs by providing stable and durable electrical conductivity without compromising mechanical strength, helping to create next-gen materials with enhanced functionality and durability.